Is East Tennessee poised to become America’s quantum hub? Experts say yes.
Between the Quantum network at Oak Ridge National Laboratory and in Chattanooga, East Tennessee is one of few states to have two hubs.
Quantum is real, and it’s coming soon. The limits of quantum are unknown, and the possibilities are endless.
Think about any optimization problem – good or bad. As an example, quantum could help solve issues with logistics companies like UPS. It could create thousands of custom routes in seconds to save time, money, emissions, and labor costs. Similarly, a bad actor example is that quantum computers could decrypt passwords, security codes, and measures in the blink of an eye, potentially crumbling countries across the globe.
Of course, the goal is for good actors to develop and harness this technology before the bad actors. Several good companies and organizations in East Tennessee are working toward that goal in two different hubs – Knoxville and Chattanooga.
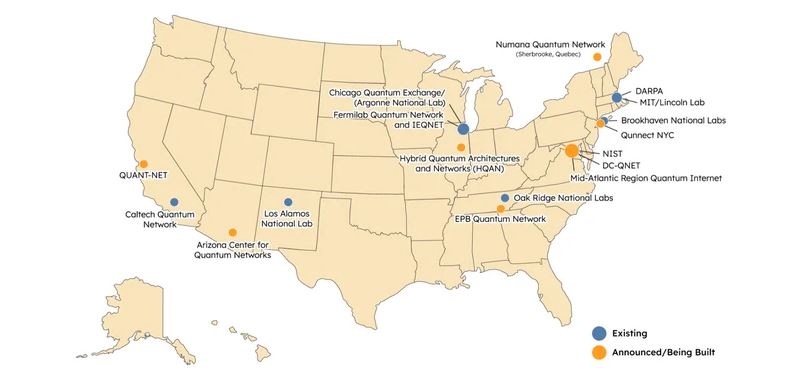
Tennessee is one of five states with two quantum networks, whereas the majority of states don’t even have one. Furthermore, both the quantum network at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) and the EPB Quantum Network in Chattanooga are located in the eastern portion of the state.
During a Knoxville Chamber panel on the Quantum Age, the idea of being at the forefront of the Quantum revolution wasn’t discussed as a pipedream, it was discussed as a reality.
“We believe East Tennessee is on the cusp of something significant,” said Dr. Travis Humble, the Director of the Quantum Science Center at ORNL during the panel. “We need to get past asking whether this technology is worth investing in, and begin asking what kind of problems we can solve with it.”
A briefing on quantum
Quantum refers to the study of matter at the level of atoms and subatomic particles. Researchers are looking at two key properties: entanglement and superposition. Superposition is a phenomenon in quantum computing that allows quantum objects to exist simultaneously in more than one state or location. It enables the qubits of the quantum computer to perform multiple operations simultaneously, making them faster than conventional computers.
When two or more particles become entangled, the state of one particle becomes linked with the state of the other(s), regardless of the distance between them. Entangled qubits in a quantum computer can be manipulated collectively, allowing for the parallel processing of information in a way that classical bits cannot achieve.
The superposition and entanglement of particles allow for much more complex outcomes than we can manipulate with zeros and ones in traditional computers.
Danna Bailey was the presenter leading the educational discussion about quantum. She is a part of the Chattanooga Quantum Collaborative and the Chief Communications Officer for Qubitekk.
“If you are amazed by artificial intelligence… just wait for quantum computing,” she said.

She showed an example of a complicated maze. A traditional computer would send a “mouse” down one avenue at a time until it found the proper pathway out of the maze. However, a quantum computer could deploy multiple mice to run in every direction, and track which ones solve the maze with the fastest routes and possible combinations.
“Frontier at ORNL is the fastest supercomputer in the world, and it can solve a hypothetical maze fast. But, it can still only run one simulation at a time,” Bailey said.
Quantum possibilities
The research is unprecedented, and exciting, and opens the doors for new solutions to complex problems. Some of the industries with optimization issues that could benefit from quantum are logistics – creating custom routes, investing and insurance- using predictive analysis to optimize portfolios and policies, cybersecurity – to protect data from all directions of attacks, and drug discovery – to cross different molecules and chemical compounds to speed up the process of pharmaceutical cures and therapeutics,
The latter example is one of the most anticipated uses of quantum computing. Right now, research and development (R&D) is so fundamental that pharmaceutical companies spend 15 percent of their sales on R&D. According to McKinsey and Company, “experts predict that today’s $200 billion market for protein-based drugs could grow by 50 to 100 percent in the medium term if better tools to develop them became available.”
McKinsey and Company predicted global pharma’s spending on quantum in R&D to be in the billions by 2030.
“Wherever there’s an optimization problem, there’s a quantum solution,” she said.
What’s next for East Tennessee and Quantum?
The city of Chattanooga laid out a 10-year goal to create $5 billion in community benefit through the development of a public quantum network. Additionally, the city, alongside the help of the Chattanooga Quantum Collaborative has a goal to prepare about 5,000 people for the quantum workforce. Bailey said a piece of the puzzle is getting more people trained in engineering, precision fabrication, and physics.
In Knoxville, the quantum realm is pretty exclusive to the national lab; however, more start-up companies are emerging to bring quantum concepts to market.
Like what you've read?
Forward to a friend!

